Acne

Acne is a common skin condition caused by the blockage of hair follicles by sebum (oil), dead skin cells, and bacteria. The blocked pores lead to whiteheads, blackheads, inflammatory papules or nodules (red, tender bumps), pustules (pus-filled bumps), and even cysts. Acne breakouts can occur at any age but are most common during the teenage years. Hormonal changes, certain medications, and the use of oily or greasy products are some factors that can contribute to breakouts. Acne breakouts most typically occur on the face, chest, back, and shoulders. Numerous treatment options are available, including but not limited to: over-the-counter products, prescription topical medications, oral prescription medications, photodynamic therapy, chemical peels, and laser therapy.
Boils
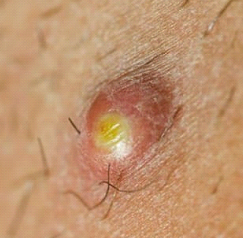
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a painful, pus-filled bump that results from a bacterial infection of the hair follicle. It is a common skin infection, typically caused by a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus. The infection usually starts as a tender, pinkish-red, bump which fills with pus- becoming larger and more painful. The boil can rupture and subsequently drain. Treatment options include warm compresses, incision, and drainage, as well as topical and/or oral antibiotics.
Cysts
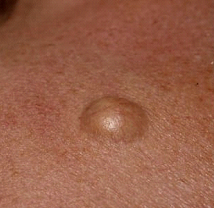
Cysts are one of the most common benign skin growths. A cyst consists of a sac or enclosed capsule filled with fluid or semisolid material. Typically, they are round or dome-shaped, with nodules or lumps on or underneath the skin. The overlying skin can be unchanged or have a small opening or punctum. They can be found anywhere, but the scalp, neck, and back are common locations. When pressure is applied to the cyst, a malodorous, cheesy discharge can be expressed. Though cysts are benign and not harmful, the lesions can at times, become inflamed, mimicking the signs of a skin infection. The affected area can become painful and red. Treatment options for an inflamed cyst include warm compresses, oral antibiotics, intralesional steroid injections, and/or incision and drainage. Definitive cyst treatment involves surgical excision, including removal of the entire sac or capsule to prevent a recurrence.
Eczema (Dermatitis)
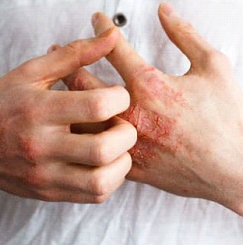
Eczema refers to a group of conditions characterized by dry, inflamed, and itchy skin. The most common kind of eczema is atopic dermatitis. Other forms of eczema include contact dermatitis, irritant dermatitis, nummular dermatitis, and dyshidrotic eczema. The term eczema is often used by people to refer to any of these conditions.
Treatment depends on the type of eczema but includes topical moisturizers, topical steroids, and systemic medications if needed.
Moles (Nevi)
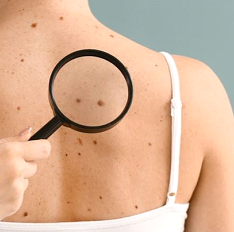
A mole, also known as a nevus (plural: nevi), is a very common skin growth. Moles develop as a result of clusters of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) in the skin. Although a mole can be present at birth (called a congenital nevus), most nevi appear during childhood and adolescence. Most people have between 10-40 moles. Moles can vary in size, shape, and color. Common moles are typically round or oval in shape. Though they can be various colors (pink, flesh-colored, tan, brown, blue, or black), most moles are uniform and homogeneous in color. Moles can be flat or raised and occur anywhere on the body. Some people can have moles that are more atypical in appearance - commonly referred to as atypical moles or dysplastic nevi. Atypical moles can be larger, more irregular in shape, and with more color variation. Though atypical moles are benign and not cancerous, they can be more difficult to differentiate from a deadly form of skin cancer called melanoma.
Visit your dermatologist if you notice any new, unusual, changing, or symptomatic moles.